Open Server Admin from the /Applications/Server folder. Double-click the name of a server in the left column to bring up the login screen. If you don’t see your server, click the Add (+) button in the lower left and select Add Server from the pop-up menu. Seamless control of servers running Mac OS X Server. Admin Tools uses a GUI for ease of configuration. The 10.6.4 version can administer servers running both 10.5 and 10.6 versions of the Apple. Apple rolled out updates for its Server Admin Tools along with Mac OS X 10.5.3 on Wednesday. OS X Server Admin Tools 10.5.3 includes fixes for all of the apps in the suite, and also bundles in. At scale, large Mac deployments often require a unique set of skills and tools to be successful. The same goes for applying management policies to Macs, which I cover in this article.
-->Applies to: Windows Admin Center, Windows Admin Center Preview
Windows Admin Center is a locally deployed, browser-based app for managing Windows servers, clusters, hyper-converged infrastructure, as well as Windows 10 PCs. It is a free product and is ready to use in production.

To find out what's new, see Release history.
Download now
Download Windows Admin Center from the Microsoft Evaluation Center. Even though it says “Start your evaluation”, this is the generally available version for production use.
For help installing, see Install. For tips on getting started with Windows Admin Center, see Get started.
You can update non-preview versions of Windows Admin Center by using Microsoft Update or by manually downloading and installing Windows Admin Center. Each non-preview version of Windows Admin Center is supported until 30 days after the next non-preview version is released. See our support policy for more info.
Windows Admin Center scenarios
Here are a few things you can use Windows Admin Center for:
Simplify server management Manage your servers and clusters with modernized versions of familiar tools such as Server Manager. Install in under five minutes and manage servers in your environment immediately, no additional configuration required. For details, see What is Windows Admin Center?.
Work with hybrid solutions Integration with Azure helps you optionally connect your on-premises servers with relevant cloud services. For details, see Azure hybrid services
Streamline hyperconverged management Streamline management of Azure Stack HCI or Windows Server hyperconverged clusters. Use simplified workloads to create and manage VMs, Storage Spaces Direct volumes, Software-Defined Networking and more. For details, see Manage Hyper-Converged Infrastructure with Windows Admin Center
Here's a video to give you an overview, followed by a poster giving more details:
Contents at a glance
Understand | Plan
|
Deploy | Configure |
Use | Connect to Azure |
Support | Extend |
Video-based learning
Here are some videos from Microsoft Ignite 2019 sessions:
Here are some videos from Windows Server Summit 2019 sessions:
And here are a few additional resources:
See how customers are benefitting from Windows Admin Center
| '[Windows Admin Center] has decreased our time/effort in managing the management system by over 75%.' - Rand Morimoto, President, Convergent Computing |
| 'Thanks to [Windows Admin Center], we can manage our customers remotely from HTML5 portal without problem and with the full integration with Azure Active Directory, we are able to increase the security thanks to the Multi-Factor Authentication.' - Silvio Di Benedetto, Founder and Senior Consultant, Inside Technologies |
| “We have been able to deploy [Server Core] SKUs in a more effective way, improving resource efficiency, security and automation while still achieving a good degree of productivity and reducing errors that can happen when relying on scripting only.” - Guglielmo Mengora, Founder and CEO, VaiSulWeb |
| “With [Windows Admin Center] customers especially in the SMB market now have an easy to use tool to manage their internal infrastructure. This minimizes administrative efforts and saves a lot of time. And the best of it: there are no additional license fees for [Windows Admin Center]!” - Helmut Otto, Managing Director, SecureGUARD |
Related products
Windows Admin Center is designed for managing a single server or cluster. It complements but does not replace existing Microsoft monitoring and management solutions, such as Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT), System Center, Intune, or Azure Stack.
Stay updated
Server Admin in OS X Lion Server handles more complex tasks than does the Server app. Server Admin provides more options and much more fine-grained control over the services it supports.
Server Admin also gives you access to services that aren’t available in the Server app, such as the DNS and push notification servers, firewall, and the software update server. Server Admin also can keep track of multiple servers and the services they’re running.
Configure services with Lion Server Admin
You can use Server Admin to configure and manage Lion Server’s many services, including Open Directory. To get Server Admin running for the first time, follow these steps:
If you’re not already logged in to the server Mac, log in as the local administrator.
Open Server Admin from the /Applications/Server folder.
Double-click the name of a server in the left column to bring up the login screen.
If you don’t see your server, click the Add (+) button in the lower left and select Add Server from the pop-up menu.
Type the hostname of the server (if not already displayed) in the Address field and then enter the administrator’s username and password.
For best results, always enter the server’s fully qualified hostname. You can also enter the server’s name ending in .local, if this is what you created when you installed Lion Server because DNS wasn’t running on your network.
Click Connect.
You’re now connected to the server and ready to manage its services. Click the triangle next to the server’s name to view an expanded list of enabled services.
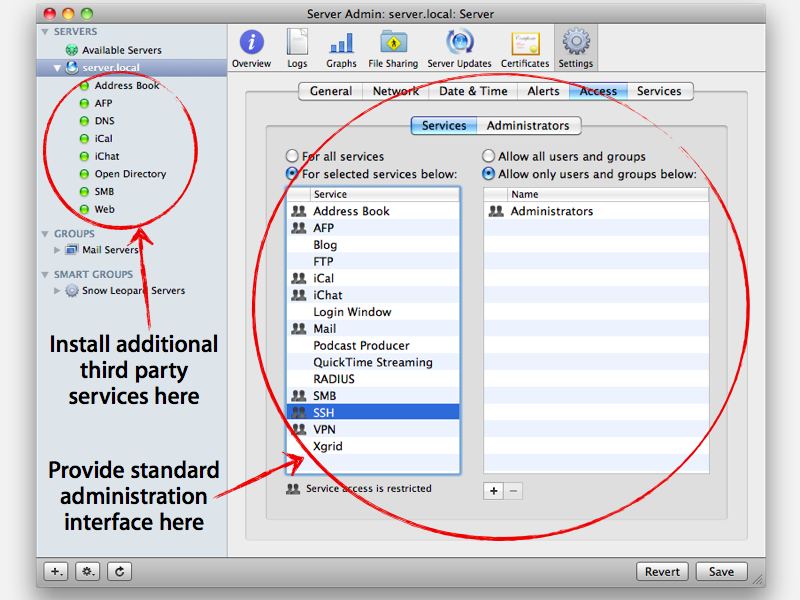
If the service you want to configure doesn’t appear in the list, it isn’t turned on. In Server Admin, a service first needs to be turned on, and then it also needs to be started. Here’s how to turn a service on:
In Server Admin, click your server in the sidebar to select it.
Click the Settings icon in the toolbar and then click the Settings tab.
Select the check box next to your service and click the Save button in the lower right.
Your service should now appear in the left column under Services.
A dot next to each service in the list can be a few possible colors:
Clear: Service is enabled but not running.
Red: Service has an error.
Light green: Infrequent, shown sometimes as a service restarts.
Dark green: Service is running normally.
Typically, you want to configure settings for a service when it isn’t running (with a clear dot). After you’re finished with the settings, you can start the service running:
Click the triangle to the left of your server to expand the list of services and then click the name of your service.
Click the Start button in the lower left of the screen.
Monitor your server with Server Admin
Server Admin provides more monitoring features than the Server app. You can access them by clicking your server in the left column to select it. The General pane appears, providing information about the host Mac’s hardware and software configuration and status.
Admin Tools Windows 10
The Logs icon gives you access to several types of log files for the server. The Graphs icon provides live graphs of processor usage and network traffic. The Server Update icon lists the previous updates to Mac OS X Server and lets you update from this window.
